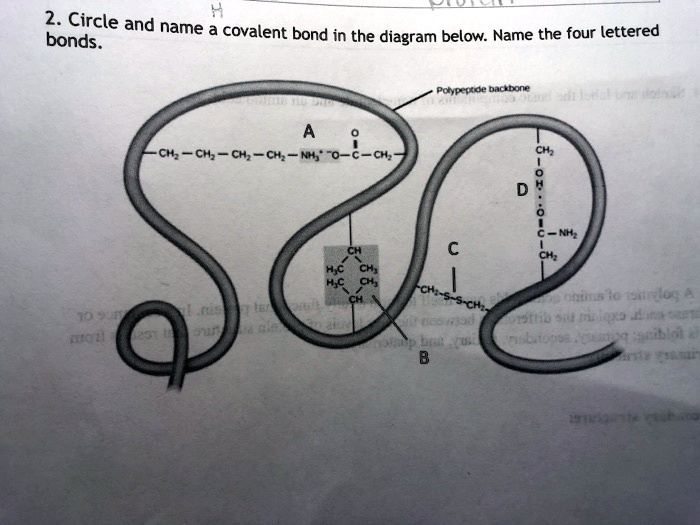
41 covalent bonding diagram
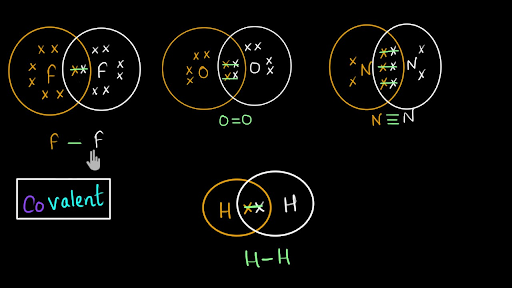
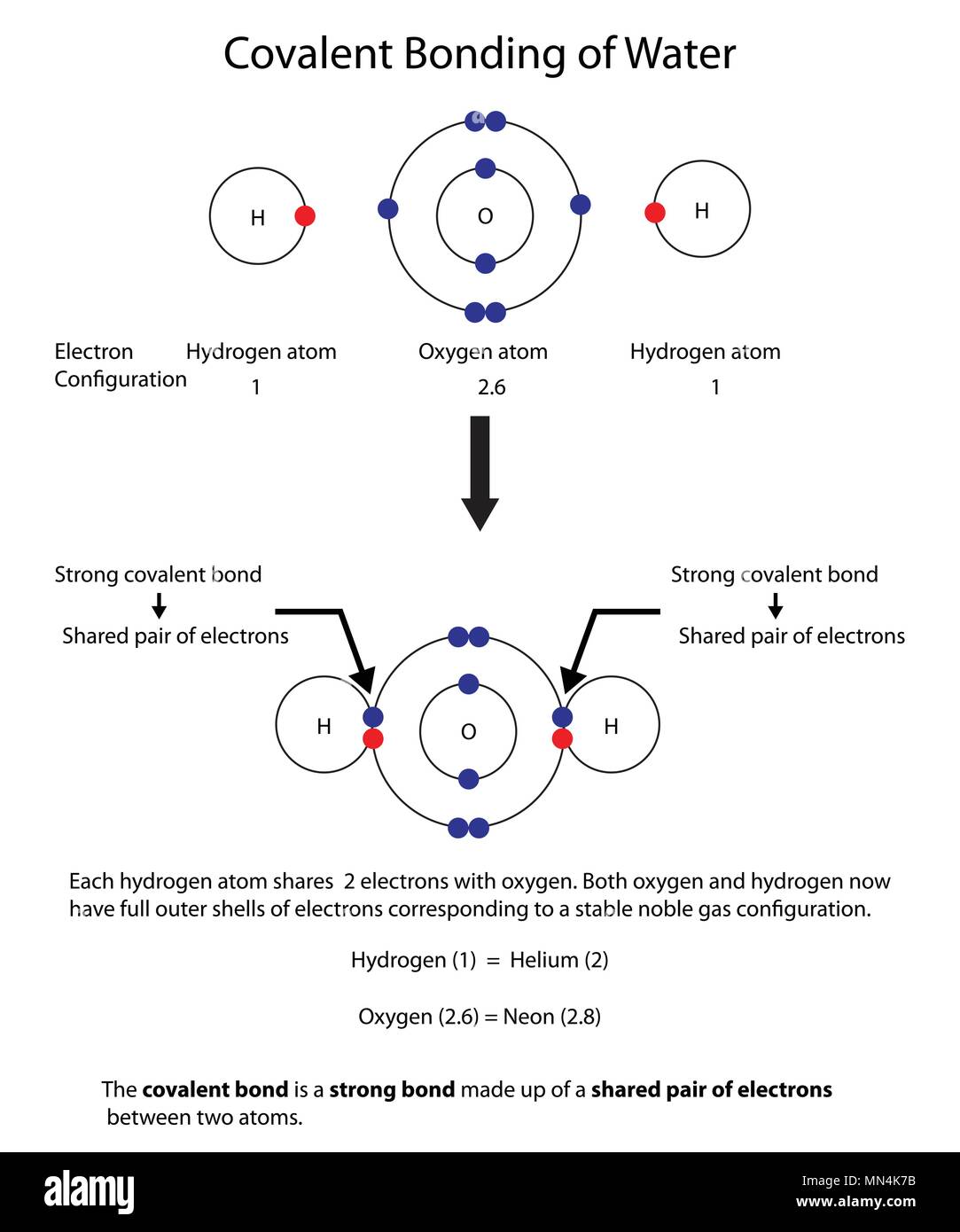
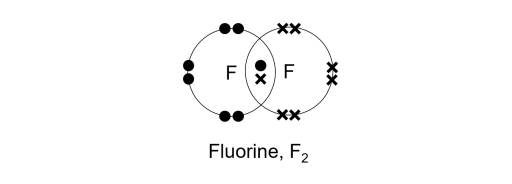
How to Draw Covalent Bonding Molecules - YouTube video explains how to draw covalent molecules and compounds. Contents:0:08 Introduction 0:39 H21:25 HCl2:23 Cl2... Covalent Bond: Definition & Example, Dative, Diagram A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. It forms between two nonmetals and usually results in both atoms having full outer shells. We can represent covalent bonds using dot and cross diagrams, which show the outer shell of electrons.
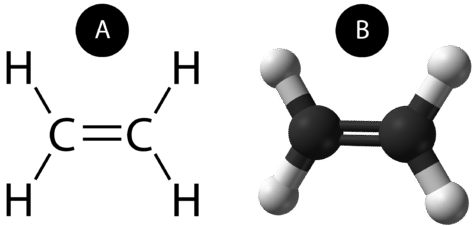
Covalent Bond - Definition, Types, Properties, and Examples Covalent bonds are directional where the atoms that are bonded showcase specific orientations relative to one another. Most compounds having covalent bonds exhibit relatively low melting points and boiling points. Compounds with covalent bonds usually have lower enthalpies of vaporization and fusion.

Covalent bonding diagram
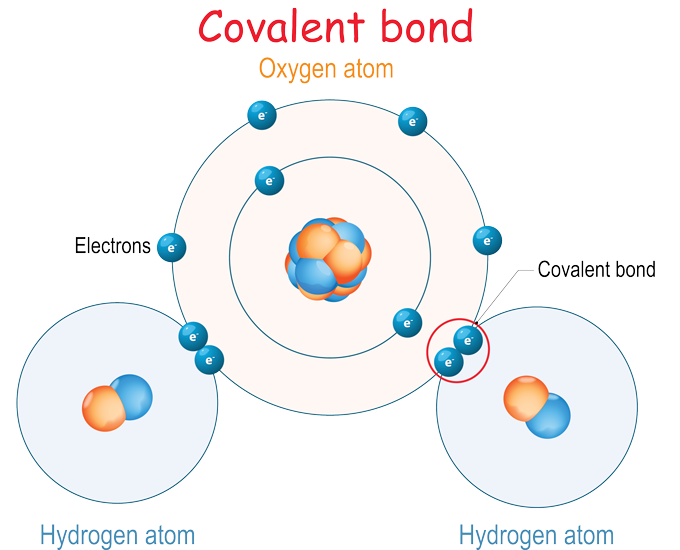
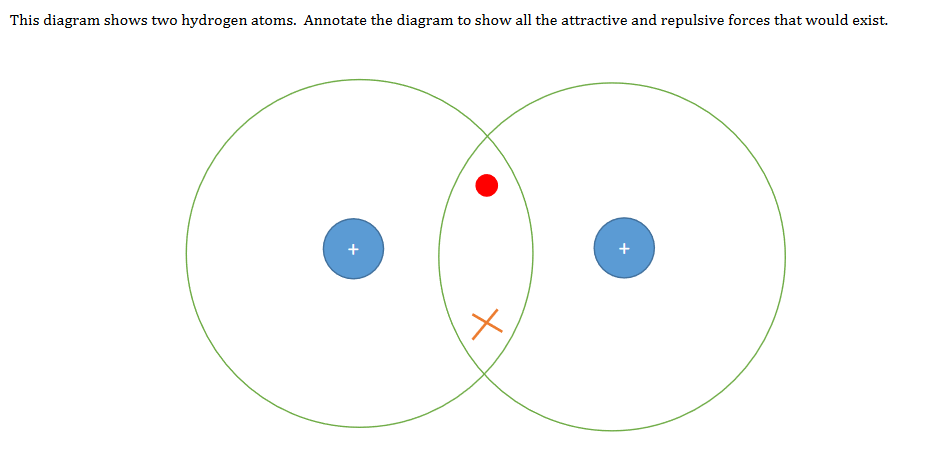
Covalent bonding - RSC Education An energy level diagram for hydrogen atoms and molecules This, together with what we already know, leads us to some simple principles for understanding covalent bonding. • Shared electrons have lower energy than unshared electrons in the same shell. • Shared electrons count towards the number of electrons allowed in the outer shell for both atoms. › GCSE › AQAChemical Bonds, Ionic, Covalent and Metallic | AQA C2 ... A covalent bond is formed when a pair of electrons are shared between two atoms (usually non-metals). Each atom must share 1 electron each to form one covalent bond - so each covalent bond is made of 2 electrons. A substance that contains atoms held together by covalent bonds is referred to as a molecule. Chapter 4: Covalent Bond and Lewis Structure - Chemistry 109 Chapter 4: Covalent Bond and Lewis Structure Ch4.1 Covalent Bond. In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent ...
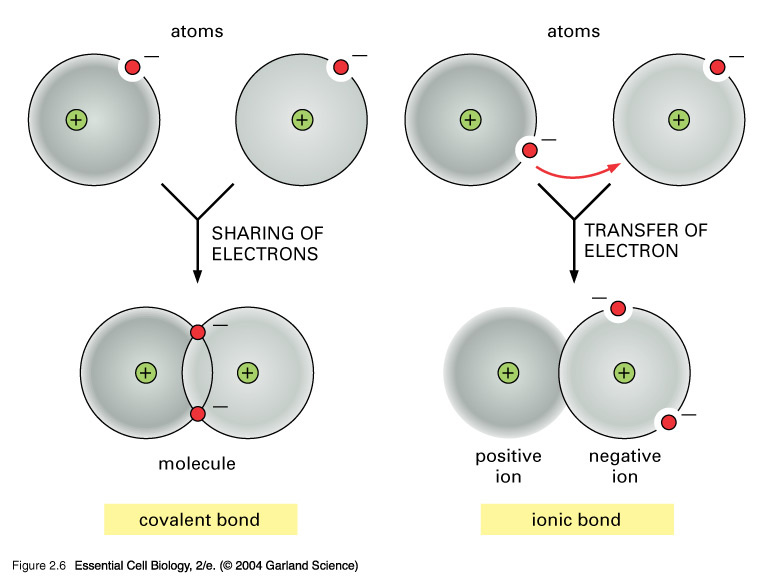
Covalent bonding diagram. Covalent Bond-Definition, Types, Examples, Diagrams ... A bond formed by the mutual sharing of electrons is a covalent bond. During the formation of a covalent bond, the two combining atoms contribute an equal number of unpaired electrons for sharing. The shared electrons belong equally to both the atoms forming the bond and completing their valence shells. 8+ Covalent Bond Types Of Atoms: Detailed Insights And Facts The structure has two chlorine atoms in the structure which form covalent bond. The covalent bonding can be explained by using lewis dot structure concept. The valence electrons in chlorine atom is 7, since there are 2 atoms of chlorine the total chlorine valence electrons will be 7×2=14 electrons. › topics › chemistryCovalent Bond - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics A covalent bond consists of the simultaneous attraction of two nuclei for one or more pairs of electrons. The electrons located between the two nuclei are bonding electrons. Covalent bonds occur between identical atoms or between different atoms whose difference in electronegativity is insufficient to allow transfer of electrons to form ions. Chapter 4: Covalent Bond and Lewis Structure - Chemistry 109 Chapter 4: Covalent Bond and Lewis Structure Ch4.1 Covalent Bond. In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent ...
› GCSE › AQAChemical Bonds, Ionic, Covalent and Metallic | AQA C2 ... A covalent bond is formed when a pair of electrons are shared between two atoms (usually non-metals). Each atom must share 1 electron each to form one covalent bond - so each covalent bond is made of 2 electrons. A substance that contains atoms held together by covalent bonds is referred to as a molecule. Covalent bonding - RSC Education An energy level diagram for hydrogen atoms and molecules This, together with what we already know, leads us to some simple principles for understanding covalent bonding. • Shared electrons have lower energy than unshared electrons in the same shell. • Shared electrons count towards the number of electrons allowed in the outer shell for both atoms.











.png)











Comments
Post a Comment