42 co2 mo diagram
Co2+ Orbital Diagram - schematron.org Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions - Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2+, Rh2+, Ni3+, etc.. σ-ML4 Tetrahedral MO Diagram e. Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Molecular Orbitals for CO2 - Newcastle University MO Calculation These orbitals were calculated at a low ab initio level (rhf/3-21g*) which can, however, show bond polarisation and fully delocalised molecular orbitals At the much higher level df/6-311g(2df) the calculated molecular orbital models look very similar, but the weakly antibonding MO σC(2 p )O(2 p ) appears below the bonding π ...
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia 4) or carbon dioxide ( CO 2 ), a MO diagram may show one of the identical bonds to the central atom. For other polyatomic molecules, an MO diagram may show one or more bonds of interest in the molecules, leaving others out for simplicity.
Co2 mo diagram
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. PDF MO Diagrams for Linear and Bent Molecules Carbon Dioxide by Reducible Representations Γ2s= Ag+ B1u Γ2pz= Ag+ B1u Γ2px= B2g+ B3u Γ2py= B3g+ B2u B3u B2u Ag Ag 2p x 2p y 2p z 2s B2g B3g B1u B1u These are the same group orbital symmetries that we got using inspection. We can (re)draw them. 5. Find matching orbitals on central atom Ag B1u B3u B2u 6. Build MO diagram… Molecular Orbitals for Carbon Monoxide - Newcastle University The MO models shown on this web page were obtained at the RHF/3-21G* level in a conventional ab initio calculation, using a Gaussian atomic basis set; This is an approximation to Natural Atomic Orbitals, 2s, 2p z, etc., which are not very amenable to computation; A Natural Bond Orbital analysis of the resulting MOs produced a set of NAOs and the coefficients of these needed to make the ...
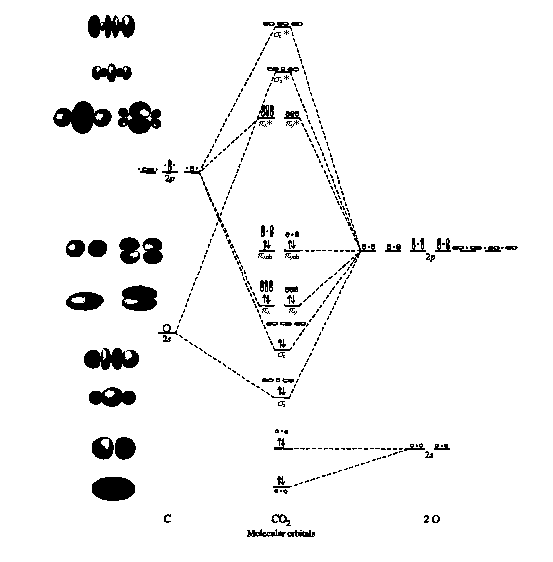
Co2 mo diagram. Draw MO diagram of CO and calculate its bond order ... Draw MO diagram of CO and calculate its bond order. chemical bonding; class-11; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. 1 Answer +1 vote . answered Dec 17, 2020 by Maisa (45.8k points) selected Dec 18, 2020 by Panna01 . Best answer. 1. Electronic configuration of C atom: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2. ... CO32- Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... CO32- Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram What is MO theory? Molecular Orbital Theory is a concept of quantum mechanics that is used to decipher the chemical bonding nature inside different molecular structures. This is a complex yet useful tool that helps in sketching MO diagrams for better understanding. Molecular orbital theory(mot) of SF6/CO2/I3-/B2H6 The molecular orbitals for the CO2 (O1=C=O2) molecules are given by, in order of increasing energy 14. CO2 MOs MO Diagram for CO2 C 2p C 2s bonding MOs antibonding MOs C AOs O LCAOs 1 3 u 3 g 2 u 1 g 1 u 2 u 2 g 1 u 1 g 15. Carbon Oxides - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Carbon dioxide is electron-poor at the central carbon and acts as an electrophile. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen.
By writing molecular orbital configuration for NO,CO,O2 ... "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram. Co2+ Orbital Diagram The angular overlap diagrams for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital .. For Co2+: High-spin octahedral d7 has LFSE = -∆o. Tetrahedral d7 has. As it is sometimes explained, the statement that 4 s orbital is lower in energy than 3 d But while you fill 3 d orbital with electrons it becomes lower and lower in. Part B. Carbon Dioxide - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign The C-O bonds in carbon dioxide are polar and yet the dipole moment is zero because the 2 bond dipoles cancel each other. One thing that we can understand by looking at the structure of CO 2, is that the carbon center of the molecule must be electrophilic.An electrophile (electron-lover) is a center that is electron poor and will be attracted to centers that are electron-rich. 5.4.2: Carbon Dioxide - Chemistry LibreTexts 5.4.2: Carbon Dioxide. Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for CO 2. Step 1. Find the point group of the molecule and assign Cartesian coordinates so that z is the principle axis. Step 2. Identify and count the pendant atoms' valence orbitals. Step 3. Generate the Γ 's. Step 4.
CO2 Lewis Structure (2021 UPDATED) All You Need To Know CO2 has an AX2 molecule based on the VSEPR theory making the molecular geometry of CO2 linear. The linear molecular geometry has a symmetrical structure with bond angles of 180 degrees once it takes its linear shape. The valence shell electron pairs also cause repulsive forces hence the shape of the molecule. Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram File:MO Diagram CO2.svg - Wikimedia Commons File:MO Diagram CO2.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 406 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 162 × 240 pixels | 325 × 480 pixels | 406 × 600 pixels | 520 × 768 pixels | 694 × 1,024 pixels | 1,387 × 2,048 pixels | 420 × 620 pixels. molecular orbital theory - π Bonding in Carbon Dioxide ... Carbon dioxide. The molecule is very symmetric and one of only a few with the point group D ∞ h. That also imposes constraints on how the spatial distribution looks like. Along the molecular axis ( O − C − O) is a rotational axis of infinite fold, C ∞, as the molecule is linear. Perpendicular to that axis there is a horizontal mirror ... PDF Below is the MO diagram for CO2 - ma Below is the MO diagram for CO2. a. Complete the MO diagram by adding the electrons. b. When two electrons are added to the CO2 does the bond order increase or decrease; explain. c. What effect does removing an electron have on the bond order of CO2; explain.
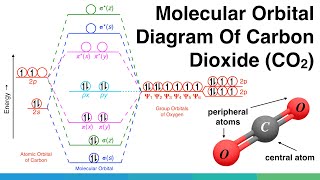
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Polyatomic CO2 Molecules ... Carbon dioxide (CO2), molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride (BeH2) However, unlike hydrogen as peripheral atoms in BeH2, there are oxyge...
Build-Your-Own Molecular Orbitals | VIPEr Description. This is a truly hands-on activity in which students manipulate paper cutouts of carbon atomic orbitals and oxygen group orbitals to identify combinations with identical symmetry and build the carbon dioxide molecular orbital diagram. The activity pairs well with the treatment of MO theory in Miessler, Fischer, and Tarr, Chapter 5.
PDF 5. Molecular Orbitals 5.1 Formation of Molecular Orbitals ... MO-Diagram for the first 10 elements: Works great for O 2-> explains O 2's paramagnetism But predicts B 2 to be diamagnetic-> Orbital Mixing! 5.2 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules 5.2 Homonuclear Diatomic ... 5.4.2 Carbon Dioxide's Molecular Orbital Diagram
Carbon Dioxide MO Diagram | Carbon dioxide (CO2) molecular ... Carbon dioxide (CO2) molecular orbital diagram (Jmol visualization) for important MOs. The HOMO-1, HOMO and LUMO+1 are degenerate and the HOMO-5, HOMO-4 and HOMO are non-bonding lone pairs. Firefly 8.2.0 DFT B3LYP 6-311++G(d,p) geometry-optimized structure (energy minimum, no imaginary frequencies). The degenerate orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Total energy = -188.6469 Hartrees. C=O ...
Solved 3) In this question, we will construct the ... - Chegg Question: 3) In this question, we will construct the molecular orbital diagram of CO2. a. The point group of CO2 is Dooh. However, for simplicity we will use the point group D2h. What are the symmetry labels for the carbon 2s, 2px 2py, and 2pz orbitals in Dan? (The character table can be found in Appendix 3 of your textbook.) b.
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Molecular orbital diagram - Infogalactic: the planetary ... For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. For simple polyatomic molecules with a "central atom" such as methane(CH 4) or carbon dioxide(CO 2), a MO diagram may show one of the identical bonds to the central atom.
CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry ... CO2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.
MO Diagram CO2 - YouTube About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Carbon dioxide - Wikipedia Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO 2) is an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas.The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm.
6.2.2: Carbon dioxide - Chemistry ... - Chemistry LibreTexts Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for CO 2. Preliminary Steps Step 1. Find the point group of the molecule and assign Cartesian coordinates so that z is the principle axis. Step 2. Identify and count the pendant atoms' valence orbitals. Generate SALCs Step 3. Generate the Γ 's Step 4.
Molecular Orbitals for Carbon Monoxide - Newcastle University The MO models shown on this web page were obtained at the RHF/3-21G* level in a conventional ab initio calculation, using a Gaussian atomic basis set; This is an approximation to Natural Atomic Orbitals, 2s, 2p z, etc., which are not very amenable to computation; A Natural Bond Orbital analysis of the resulting MOs produced a set of NAOs and the coefficients of these needed to make the ...
PDF MO Diagrams for Linear and Bent Molecules Carbon Dioxide by Reducible Representations Γ2s= Ag+ B1u Γ2pz= Ag+ B1u Γ2px= B2g+ B3u Γ2py= B3g+ B2u B3u B2u Ag Ag 2p x 2p y 2p z 2s B2g B3g B1u B1u These are the same group orbital symmetries that we got using inspection. We can (re)draw them. 5. Find matching orbitals on central atom Ag B1u B3u B2u 6. Build MO diagram…
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above.








![Reactivity of CO 2 towards Mo[N(R)Ph]3 - Dalton Transactions ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2009/DT/b909982d/b909982d-f7.gif)
![Molecular orbital interaction diagram for Re[Cl(CO2)] of Cs ...](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342215688/figure/fig5/AS:960037639970826@1605902218521/Molecular-orbital-interaction-diagram-for-ReClCO2-of-Cs-symmetry-The-populations-of.png)











Comments
Post a Comment